Cart (0 Items)
Your cart is currently empty.
View ProductsIt looks like you are visiting from outside the EU. Switch to the US version to see local pricing in USD and local shipping.
Switch to US ($)
Client
Pharmaceutic industry
Sector
Diagnostic
Research Domain
Neurology
Key Processes
A pharmaceutical company had identified a promising antibody candidate for the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases, but its sensitivity was too low for reliable detection. The goal of the project was to increase the binding affinity of a mouse antibody targeting a human antigen, to accelerate development and progress more quickly toward a robust diagnostic solution.
To de-risk and streamline the optimization strategy, we first performed detailed paratope–epitope mapping to clarify the interaction interface and guide a more rational design of affinity-improved variants. Based on these insights, we then leveraged our Affinity Maturation service to generate and screen optimized antibody variants, selecting improved candidates with stronger target binding.
Preserving backbone structural stability despite sequence changes
Approaching the performance plateau as closely as possible
Improving affinity without increasing non-specific binding
Our process consists of designing targeted mutations to enhance antibody–antigen interactions, while accounting for the specific challenges of each project.
AI-guided variant design
We used our AI platform to propose targeted amino acid substitutions, and our expertise allowed us to select 20 antibody variants to design and test.
Biological review
We systematically reviewed and challenged the AI-generated substitutions with our bioinformatics team to ensure each variant was biologically relevant and aligned with their target requirements.
Laboratory validation
We expressed and purified the predicted variants, then validated binding using SDS-PAGE, ELISA titration, and biolayer interferometry (BLI) to generate empirical affinity metrics for their lead selection.
Iterative learning loop
We fed the experimental results back into our AI models, enabling rapid design–test iterations and faster convergence toward lead antibody candidates with improved affinity.
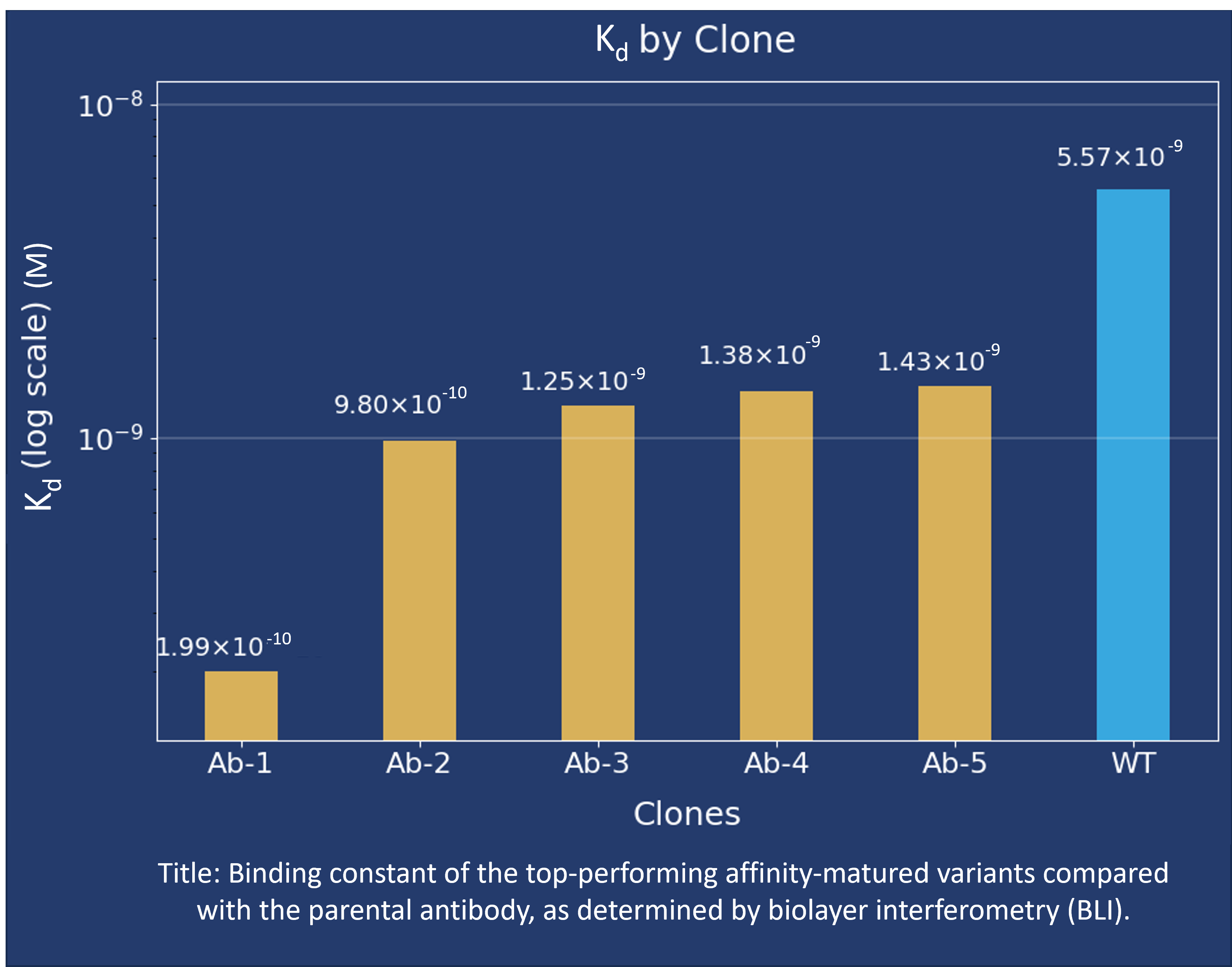
We successfully identified a lead antibody variant (Ab-1) showing an approximately 20-fold improvement in binding affinity relative to the parental antibody (WT), along with additional affinity-improved variants (Ab-2 to Ab-5) exhibiting 2- to 10-fold increases in affinity compared with WT.
Kinetic measurements indicated that affinity maturation did not compromise the antibody’s initial performance and maintained developability. In addition, 3D structural analysis combined with our AI tool confirmed backbone structural stability.
The customer obtained antibody variants with up to a 20-fold increase in affinity compared with the parental antibody, enabling faster and more confident progression to the next stage of the project.
Our AI-powered affinity maturation approach predicts and introduces targeted mutations to enhance antigen binding while preserving the antibody’s developanility.